Mobile Governance (m-governance): Mobile governance(m-governance) aims to leverage wireless and new media technology platforms, mobile devices and applications for delivery of public information and services to all citizens and businesses. It aims at widening the reach of, and access to, public services to all citizens in the country, especially in the rural areas by exploiting the much greater penetration of mobile phones in the country. It also leverages the innovative potential of mobile applications in providing public services.The overall strategy aims at making India a world leader in harnessing the potential of mobile governance for inclusive development. The initiative has been conceptualized and formulated by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India. Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), a MeitY organization, is the technical implementing agency for the project.
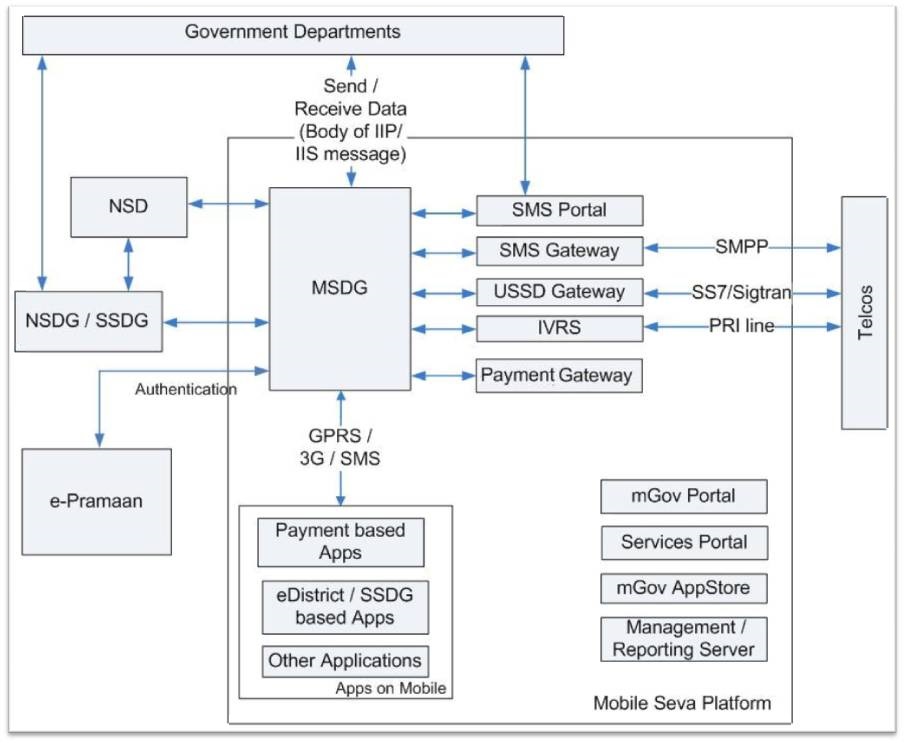
Mobile Seva is an innovative initiative aimed at mainstreaming mobile governance in the country. It provides an integrated whole-of-government platform for all Government departments and agencies in the country for delivery of public services to citizens and businesses over mobile devices using SMS, USSD, IVRS, CBS, LBS, and mobile applications installed on mobile phones.The diagram below depicts the various components of Mobile Seva.
Considering the huge penetration of mobile phones in the country especially in the rural areas, it has become imperative to offer government services over mobile-devices to ensure that the vision of the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) to provide government services to citizens near their doorsteps becomes a reality. Mobiles can become the most common access devices for government services provided through the national e-Governance exchange middleware comprising National e-Governance Services Delivery Gateway (NSDG), State e-Governance Services Delivery Gateway (SSDG) and various domain gateways, e.g. Passport Gateway, MCA21 Gateway, etc. The current architecture of NSDG/SSDG or the domain gateways should be supplemented with a framework for mobile governance.
A separate infrastructure for Mobile Seva is
required as:
1. Seamless integration with backend
department needs to be ensured through existing NSDG/SSDG eGov
exchange infrastructure.
2. Common interface needs
to be provided for various mobile based services, e.g., Short
Message Service (SMS), USSD (Unstructured Supplementary Service
Data), IVRS (Interactive Voice Response System), CBS (Cell
Broadcasting Service), LBS (Location Based Services), mobile
applications, etc.
3. There is a need to generate
as well as render the contents for delivering services on the
mobile platform as mobile devices present a constrained
environment.
The MSDG enables delivery of public services over mobile devices through various mobile based
channels, such as SMS, USSD, IVRS and mobile applications. As MSDG has been developed based on
IIP/IIS (Interoperability Interface Protocol / Interoperability Interface Specifications)
standards of Government of India, it provides seamless integration with the backend departments
through existing NSDG/SSDG eGovernance exchange infrastructure. Backend departments are
connected to the MSDG for mobile based services.
MSDG consists of the following components.
1. SMS Gateway :
The SMS Gateway provides the common service of SMS to the eGovernance exchange and is used to deliver SMS based services to all citizens and businesses. It supports both push and pull based services. Using push services, common informational services can be pushed to citizens as a group. Departments can use the SMS Portal or a programmatic interface to push SMSs to citizens. Citizens can also request for specific information through pull based SMS services. Short codes 51969 and 166 have been allotted by Government of India for mobile governance services in the country. These short codes have already been made operational for pull services. In addition, a long code, 9223166166, has also been made operational for pull services.
2. IVRS(Interactive Voice Response System):
IVRS is an example of a computer-telephone integration (CTI). The most common way for a phone to communicate with a computer is through the tones generated by each key on the telephone keypad. These are known as dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) signals. A computer needs special hardware called a telephony board or telephony card to understand the DTMF signals produced by a phone. A simple IVR system only requires a computer hooked up to a phone line through a telephony board and some IVR software. The IVR software allows pre-recording of greetings and menu options that a caller can select using his telephone keypad. More advanced IVR systems include speech-recognition software that allows a caller to communicate with a computer using simple voice commands. Speech recognition software has become sophisticated enough to understand names and long strings of numbers.In the context of mobile governance, the IVRS application is intended to serve the C2G and G2C services within the e-governance domain. Through IVRS based services, status enquiries for a large number of services can be automated and the requisite information provided to the service seekers without causing undue overheads on the e-governance infrastructure.
3. Location Based Services (LBS):-
Location Based Services (LBS) can be very useful for the departments for customizing their services according to the location of the service seeker. There are various ways in which location of the service seeker can be determined. Most popular are GPS and cell tower based locations. GPS based location is more accurate compared to cell tower based location. MSDG will connect to such systems and will provide a unified interface to departments or developers of mobile applications, which can be used by them for customizing or developing the applications.
4. Cell Broadcasting Services (CBS):-
Cell Broadcasting Services (CBS) are particularly relevant when certain notifications or alerts have to be sent to citizens in a particular area. This can be very helpful in case of disaster or emergency situations. MSDG will connect to all the telecom operators for CBS for this service and will provide a unified interface to the departments. Departments can then use this unified interface for notifications and alerts in a particular area.
5. Geo-Fencing Digital Broadcast:-
Government departments will promote their services and reach out to a significant portion of the population in an effective manner. Any new service enabled on the platform will need to be notified / popularized via Facebook social media platform. Geo fencing allows automatic alerts to be generated based on the location-based service (LBS) defined coordinates of a geographic area.
6. Mobile Seva AppStore:-
Department can host mobile application on Mobile Seva App Store (https://apps.mgov.gov.in) free of cost. Citizen can download applications from on their handsets and using these applications they can access various government services anytime from anywhere.
7. mGov App Container:-
Application allowing users to browse and download any applications that are hosted or published on Mobile Seva AppStore.
8. SmartApp Notifications:-
Government departments will push notifications are simple messages send through services portal and message will display on apps that are installed on a device based on the preference area or services domian. In the mobile Application user will received notifications wake up the handset device and alert the user with a message displayed.User can change the preferences at any point of time based on their requirements and can also see the previously saved preferences.